Hip fracture
Broken hip / femoral neck fracture / collum femoris fracture
A hip fracture refers to a broken hip. This injury usually occurs after a fall and it is virtually impossible to bear weight on the affected leg. The fracture is treated surgically.
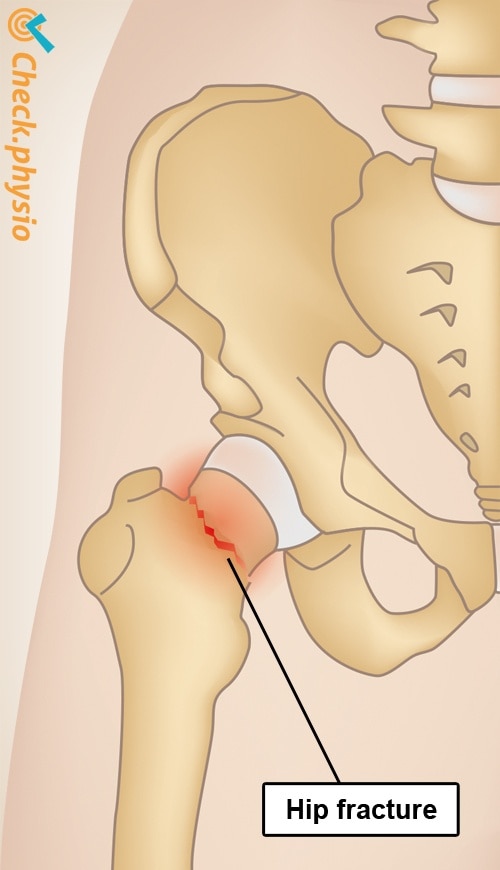
Hip fractures are very common. In the US there are about 300,000 each year. The numbers are increasing year by year. Three quarters of the people with a broken hip are aged 75 or older. Women are more likely to suffer a hip fracture than men.
Description of condition
The medical term for the thigh bone is the "femur". With a hip fracture, the femur itself is broken. Various types of break can occur. Sometimes a partial break will occur. In severe cases, the entire head of the femur breaks off and the different parts dislocate.
A hip fracture may have significant consequences, particularly for older patients. One in three patients dies in the first year after admission. The patients that do survive often lose their independence.
Cause and history
A broken hip almost always occurs after an accident or fall. For elderly people it is usually a fall. A high energy trauma is required to break the hip of younger patients. Examples include a fall from height or a frontal collision.
Signs & symptoms
- Pain in the hip after an accident or fall.
- It is virtually impossible to bear weight on the affected leg.
- Walking is impossible.
- The leg is rotated outward.
- The affected leg may be shorter than the other leg, as a result of the femur being shifted upward.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis is made based on the patient's story, a physical examination and X-rays. If the X-rays do not show a break, but a hip fracture is still suspected, an MRI scan or CT scan can provide clarification.
Treatment
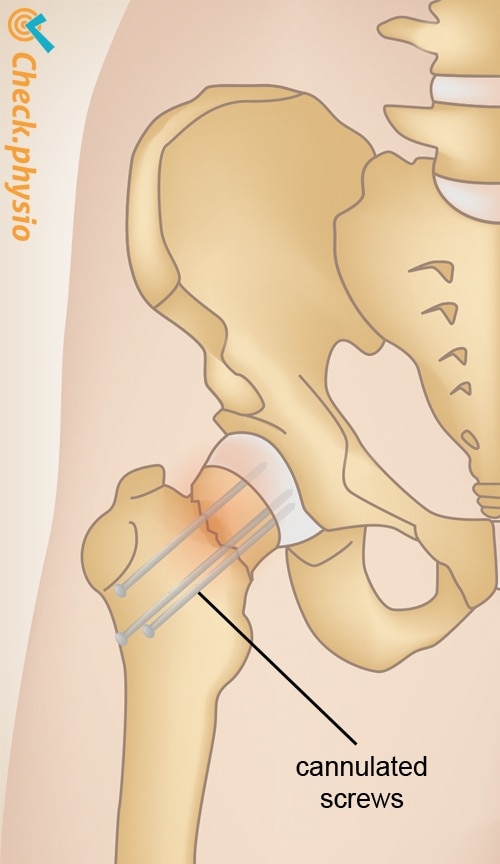
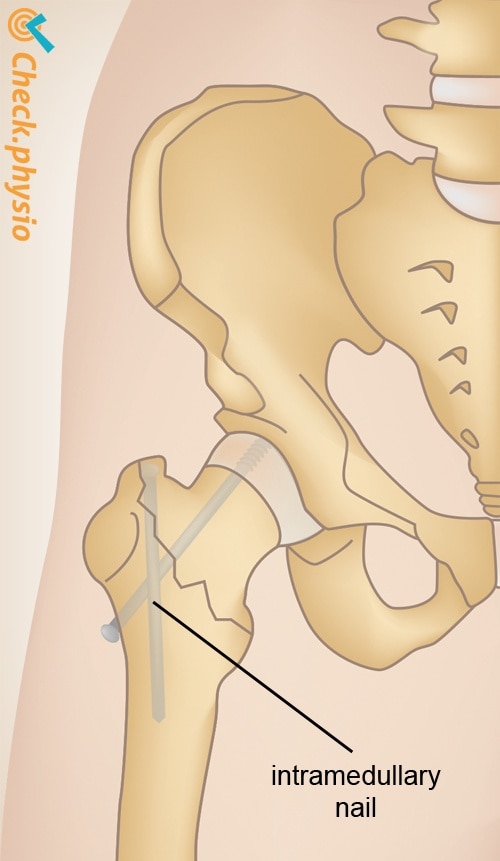
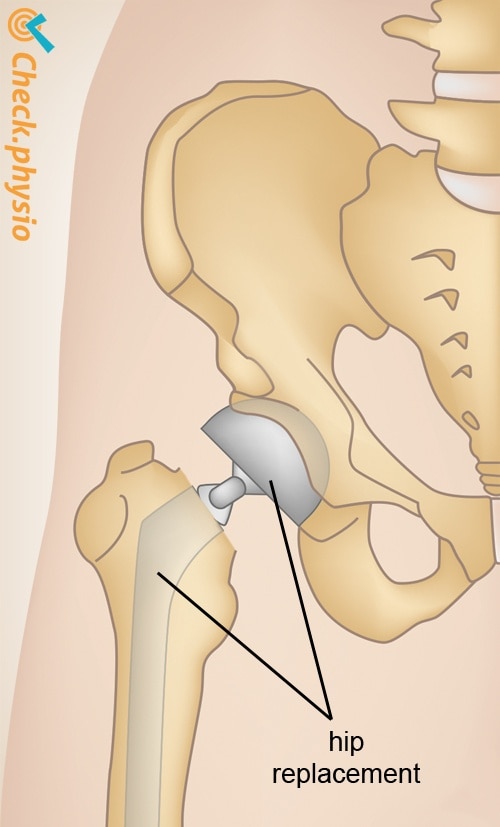
Treatment is almost always by surgery. The aim of the surgery is to secure the break in such a way that the patient can place weight on the leg again as soon as possible. Various techniques are applied, depending on the type of break. Sometimes it is decided to insert a hip prosthesis (artificial hip).
Rehabilitation takes place as soon as possible after surgery. Extended bed rest may have a negative effect on the patient's health. This includes complications affecting the lungs, loss of muscle strength and reduced stamina. The physiotherapist will supervise exercise therapy, so that the patient can ultimately walk again unaided or with a walking aid.
Exercises
You can check your symptoms using the online physiotherapy check or make an appointment with a physiotherapy practice in your locality.
References
Nationaal Kompas Volksgezondheid (2010). Heupfractuur: incidentie naar leeftijd en geslacht. Bilthoven: RIVM.
Nugteren, K. van & Winkel, D. (2007). Onderzoek en behandeling van de heup. Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Verhaar, J.A.N. & Linden, A.J. van der (2005). Orthopedie. Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.





